Photosynthesis: The Alchemy of Life
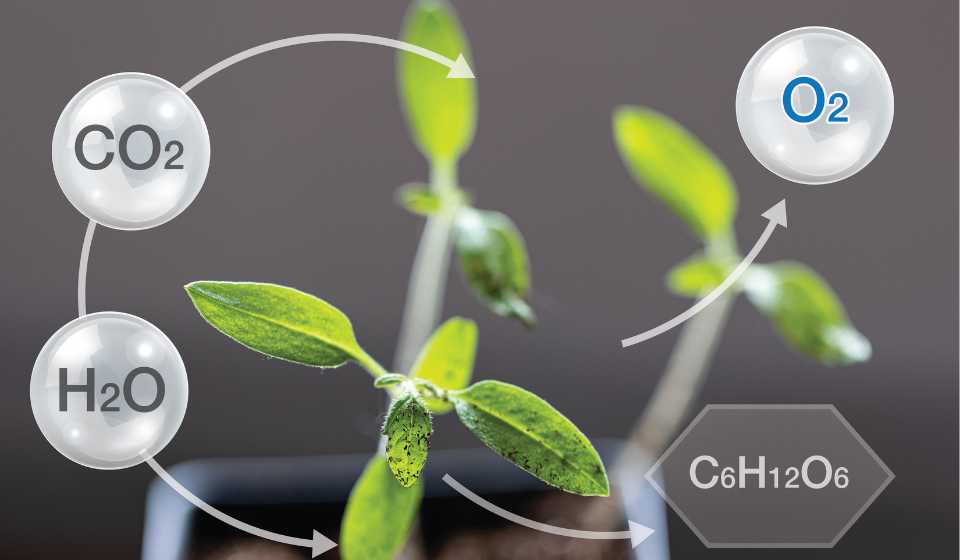
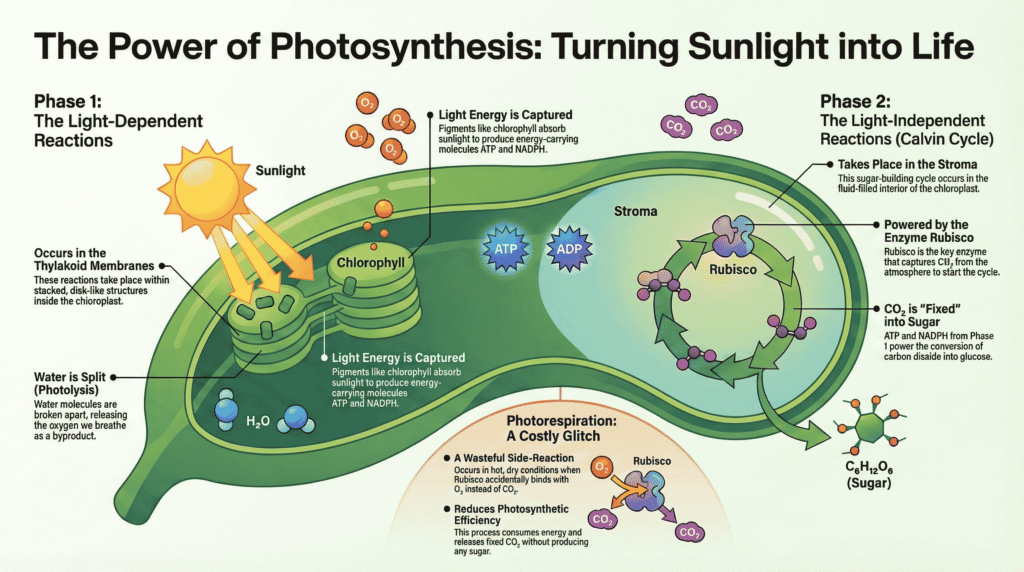
Photosynthesis is the fundamental biological process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, stored in the bonds of organic molecules like glucose. It is the primary source of organic matter and oxygen for almost all life on Earth, forming the base of nearly every food chain. 1. Photosynthesis […]
Photosynthesis: The Alchemy of Life Read More »